Having a lactose intolerance system does not have to result in a life of avoiding dairy products; there are many other ways to enjoy a lactose-free life.
Lactose intolerance affects about half the percentage of adults worldwide, which means millions of people day in day out experience bloating, cramps, and diarrhea whenever they eat food that contains lactose. Although it is not life-threatening, it causes discomfort to those who experience it.
Most people with this condition cut off dairy products or take pills to help with lactose intolerance after they become uncomfortable. There are better ways to manage the situation; read on to see alternatives to make your diet and lifestyle much better as you handle lactose intolerance.
How do I know if I am lactose intolerant?
Lactose is the sugary content found naturally in dairy products such as milk and cheese. However, the sugar content is higher in milk than in other dairy products. Hence, it is one of the significant causes of indigestion.
A person is lactose intolerant when they don’t produce the right amount of lactase, as it is an enzyme that helps digest lactose. It is also called “Lactose Malabsorption,” as the digestive system cannot fully absorb lactose into the body. This means that it does not have to be the absence of lactase but a secretion lower than the required limit.
You can also clear your doubt with a visit to the hospital, where a test will be conducted to be sure. They may perform a hydrogen breath test when your hydrogen levels are used to measure your lactose digestion after an intake of dairy products. The doctor can also test the blood for glucose level after hours of eating a food high in lactose.
Symptoms to watch out for
After eating a dairy product containing lactose, you might begin to feel discomfort between 30 minutes to 3 hours, depending on your digestive system. The symptoms may include:
- General stomach cramps
- Bloating and gas
- Rumbling stomach
- Nausea that might lead to vomiting
- Diarrhea or loose stooling
Related article: 10 best Carla Hall recipes for healthy eating.
What Causes Lactose Intolerance? – Treatment
Medically, it means lactase deficient, but three significant types classify the condition. The small intestine is the location where the fate of your bowels is decided. It is responsible for producing lactase, which digests the sugar in dairy products. When secreted in low quantity, it causes indigestion hence the discomfort.
An average level of lactase in the small intestine will convert all the lactose into glucose and galactose as this is the only way it can get absorbed from the intestinal lining into the bloodstream. The reverse is the case when the lactase secretion is low. When the lactose is not converted to sugar, the food goes down to the colon – a holding place for waste before excretion.
When the food gets to the colon, the lactose still in it becomes associated with the bacteria found in the colon. And this causes the discomfort that comes with being lactose intolerant. While the deficiency of lactase is the primary factor that causes this condition, below are three forms it can take.
1. The congenital form of Lactose Intolerance
This form of lactose intolerance is rare, but sometimes infants are born with little or no lactase production. Parents can genetically transmit it to their child due to a recessive gene carrying the condition. So, such people experience the discomfort of lactose intolerance from their infant stages due to low lactase levels naturally as a disorder.
2. Primary Form of Lactose Intolerance
In this form of lactose intolerance, a person digests lactose properly from an infant, but when they are adults, they find difficulty in digesting food rich in lactose. The decline in lactase production starts when other foods replace an entire milk diet. Since as children, the level of lactase is usually high and reduces as time goes by.
In some people, there is enough lactase left to process their lactose diets; it only becomes a primary form of lactose intolerance when the individual can no longer digest dairy products as adults.
3. Secondary Form of Lactose Intolerance
When an illness or disease is the cause of lactose intolerance in an individual, it is classified as being secondary. several diseases can affect lactase production, such as excessive bacteria growth, celiac, and certain intestine infections.
Such a disease might require surgery or other forms of treatment that can reduce lactase production. However, you can correct this condition with prolonged medications, so the lactase levels are back to normal.
How to choose a non-dairy alternative
Your diet and general wellbeing should be at the back of your mind when you shop for non-dairy milk. Before you choose, you should consider if you will need milk with high protein content, the milk is if your diet requires it, or if you have a deficiency.
Another reason why people choose regular milk is because of the calcium content. So, if you need such calcium levels in your diet, then you read the labels for a non-dairy milk that matches or comes close to that of the regular milk.
Other things to consider are the vitamin, mineral, and sugar levels of the milk alternative you are going for. As individuals, we need to watch what we put with our bodies, so when next you are shopping for food items, spend a little more time reading the labels for the ingredients contained in the milk.
The best non-dairy alternative for lactose intolerance
Milk is mainly obtained from cows and goats and it contains lactose. However, they are very rich in calcium and other essential vitamins. It is not the best for everyone, so the best alternative is to seek lactose-free dairy products. These include soy milk, almond milk, oat milk, and a lactose-free cow or other mammal’s milk.
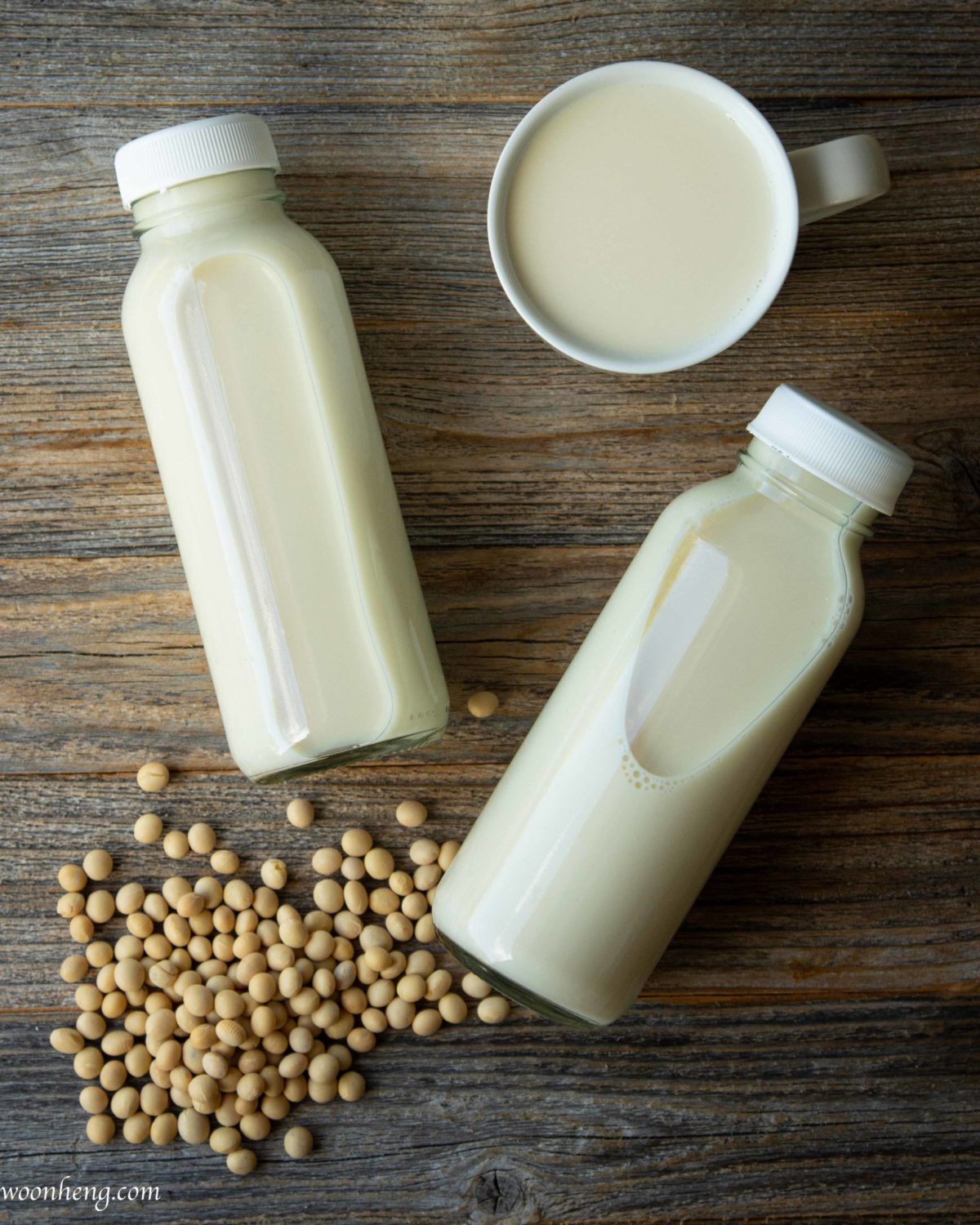
1. Soy Milk
Soy milk is one of the best alternatives to cows’ milk, as they both have almost similar content of calcium and minerals. But soy milk has a higher healthy fat range and a high protein level. They are, however, the most sought after as a vegan milk option for vegetarians but not suitable for milk allergy substitution. Soy milk is available in different varieties, as some can be sweetened and you get to choose the variant ideal for your diet.

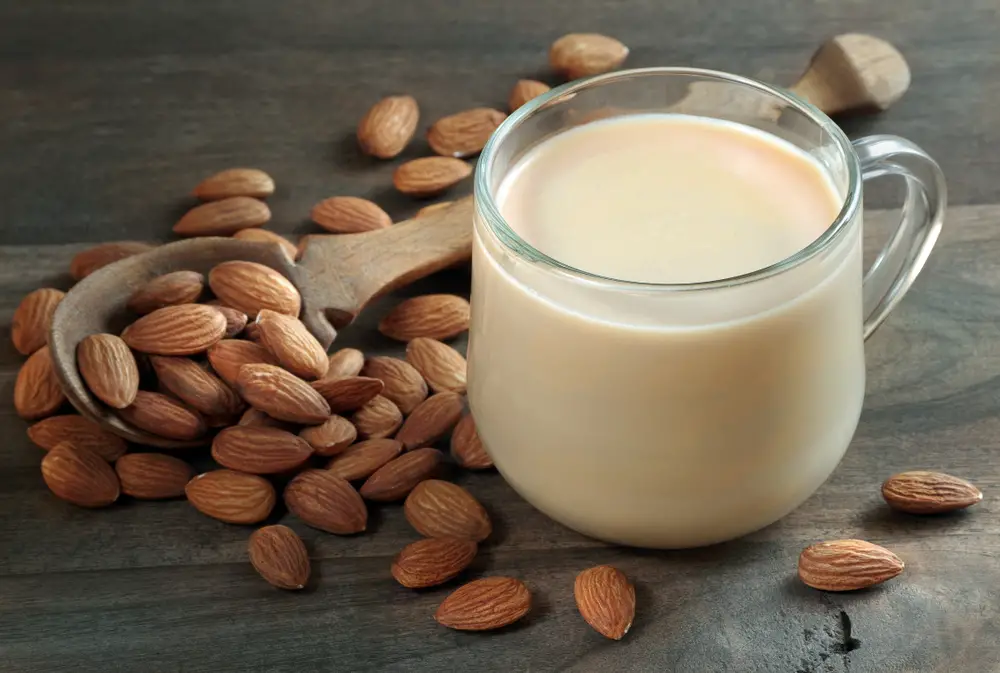
2. Nut Milk
Nuts milk such as almond and walnut milk have a higher rate of healthy fat than soy milk if you require that in your diet. Almond milk can pass up for regular milk in appearance and texture but taste differently due to the nutty aftertaste. It also contains a lower protein level than cow’s milk. However, it still has all the essential nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D. They are an excellent substitute for eating cereals, coffee, milkshakes, and all other meals you don’t mind the nut flavor.

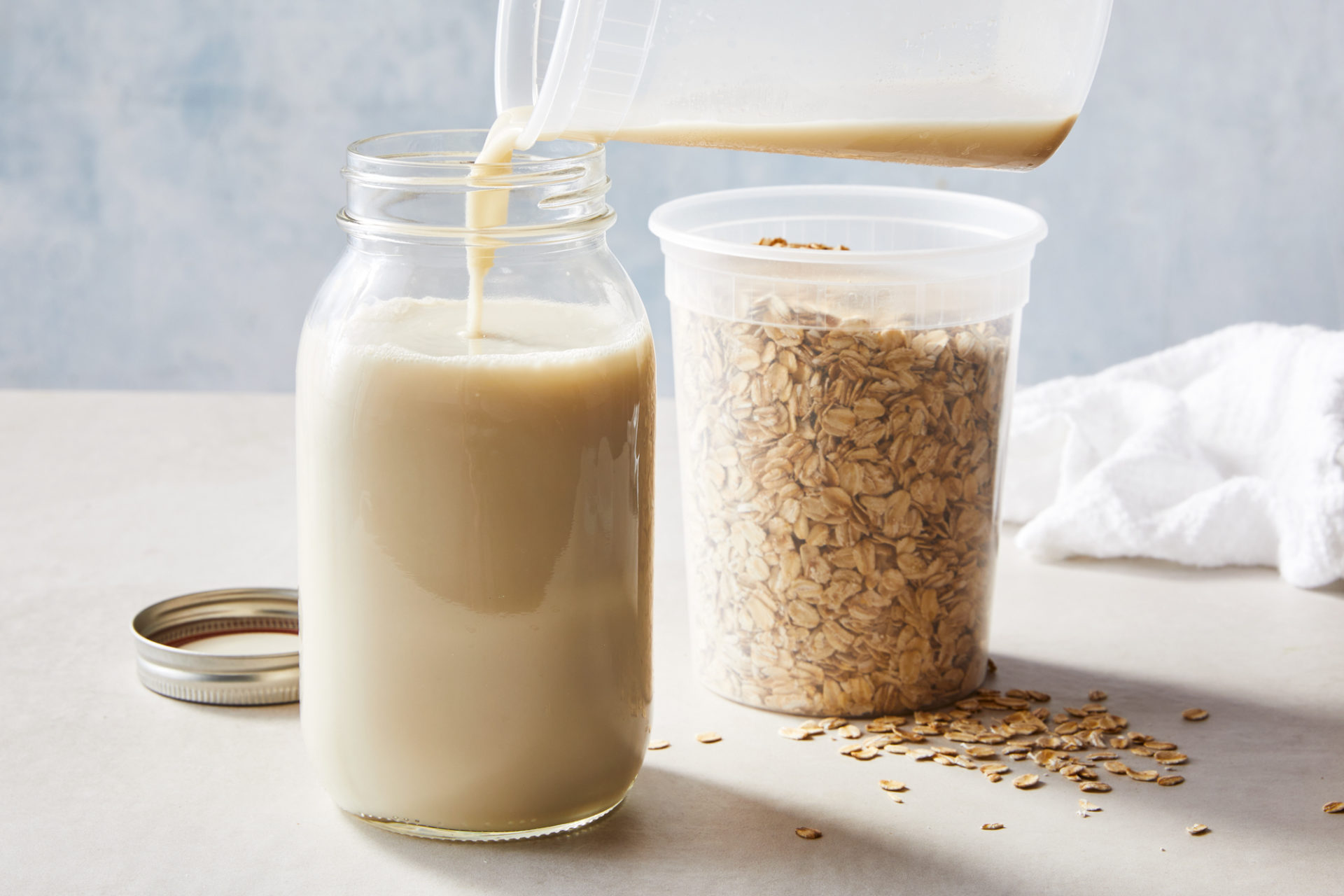
3. Oat Milk
Oat milk is your best bet if you need a diary alternative rich in fiber. It also has higher calorie content than nut and cow’s milk. They are just as fortified with nutrients as the whole oats, containing vitamins A, D, B12, and carbohydrates. Oat milk, however, has lower protein levels and can be high in sugar when sweetened. So, if you are concerned with your sugar intake, it is best to stick with the unsweetened variants.

4. Hemp Milk
This milk alternative is made from hemp seeds and has a thicker texture than cow’s milk. Asides from the grit that comes from using the milk, they are very rich in protein and omega 3. With the right amount of fatty acid that makes it highly nutritious.

5. Coconut Milk
Coconut milk gives the same dense properties when you need a complete cream alternative. They have lower protein levels than regular milk but are very rich in saturated fat. If you are sensitive to the fat contents of coconut or are looking to shed some weight, then it might not be the best option for you. Coconut milk makes a good pairing with coffee and cocoa.

Alternatives to other dairy products such as cheese are to go for the lactose-free versions, but most cheeses have a low level of lactose. For butter, you can substitute for olive oil or coconut for cooking and baking; then, you can use peanut or fruity spread as a spread. If you like to take ice-creams, always remember to go for the lactose-free brands or stick to diary-free or fruit-based ice-creams.
Conclusion
In summary, it is best to see a doctor if you are going through a lactose intolerance crisis, especially if it happens frequently. Sometimes, you might be lactose tolerant but might still find it difficult to digest dairy products with higher levels of lactose properly. So, be sure to get testing for symptoms relating to lactose intolerance and adjust accordingly. You should not be left craving for dairy products or, in the worst case being deficient in essential minerals and vitamins.
You may also like to read, 2021 Top 10 Most Searched Foods On Google That I May Try In 2022.





















About Me
Fashion & Beauty Enthusiast
Hi, I'm Fanti. I'm a fashion, beauty, and lifestyle enthusiast, and the ultimate curves queen. Here, I share beauty, fashion, and lifestyle tips to teach, inspire, and give confidence to all women.